Artificial intelligence for data science and cybersecurity
Scientific referent
Coordinator: Mohamed Nadif
Scientific leaders:
- Severine Affeldt
- Lazhar Labiod
- Ahmed Mehaoua
- Osman Salem
Presentation of the thematic area
- Machine learning for data science is an essential field of study in artificial intelligence. It comes in different forms: unsupervised, semi-supervised, supervised by reinforcement. Although multiple algorithms, models and strategies are available today, many major challenges still remain, in many different domains.
- The researchers of the team focus on several issues related to learning including (Co)-clustering and dimensionality reduction (unsupervised/semi-supervised learning) as well as supervised classification. Our work is based on different approaches such as matrix factorization, mixture models, latent block models, spectral decomposition and deep learning. Our main objective is to propose innovative models and algorithms that are efficient and easily exploitable in practice. Thus, the methods we propose are dedicated to the processing of multi-source data of different natures with applications in various domains such as textual data analysis, automatic natural language processing, bioinformatics, collaborative filtering, mediation analysis and cyber security. In addition, we are interested in the medical field, developing new machine learning methods and user-friendly software that can integrate various types of omics data to identify the players in complex human diseases.
- The researchers of the group are also developing theoretical and applied research in the area of cyber security and resource management in cyber-physical systems in particular anomaly detection for wireless medical body sensor networks. The group's contributions are oriented towards the design, optimization and performance evaluation of new protocols, algorithms, tools and formal models. They allow, thus, to provide quality, and security of communications and data, in next generation health physics systems such as chronic disease detection (Ischemia, epilepsy, etc.).
Keywords
Machine and Deep Learning ; Co-clustering ; Factorization ; Spectral Clustering ; Mixture models ; Attributed Network Embedding ; Mediation analysis ; Wireless Sensor Networks ; Internet of Medical Things ;Security and Anomaly detection ; Resource Optimization
Topics covered
- Spectral clustering via ensemble deep autoencoder learning and evaluation on image data.
- Regularized bi-directional co-clustering for biomedical texts.
- Endotypes identified by cluster analysis in asthmatics and non-asthmatics and their clinical characteristics at follow-up: the case-control EGEA study.
- Unsupervised text mining for assessing and augmenting GWAS results.
- Real-time biomedical data analysis systems based on Machine Learning (ML) and Wireless Body Sensor Networks (WBAN),
- Sensor-based remote health monitoring, Sensor-based Human activity recognition, Sensor-based Ischemia and Epilepsy detection,
- Cybersecurity threats Detection using AI/ML, Blockchain-based Anomaly and threats detection for Internet of Things (IOT).
Applications
(Co)-clustering de documents textuels
- CIKM' 2021 : How to Leverage a Multi-layered Transformer Language Model for Text Clustering: an Ensemble Approach.
- SIGIR' 2021 : Regularized Dual-PPMI Co-clustering for Text Data.
- CIKM' 2020: Ensemble block co-clustering: a unified framework for text data.
(Co)-clustering d'images
Softwares and Packages
Main publications
- Poisson degree corrected dynamic Stochastic Block Model, P. Riverain, S. Fossier, M. Nadif, Adv Data Anal Classif 17, 135–162 (2023). 2022.
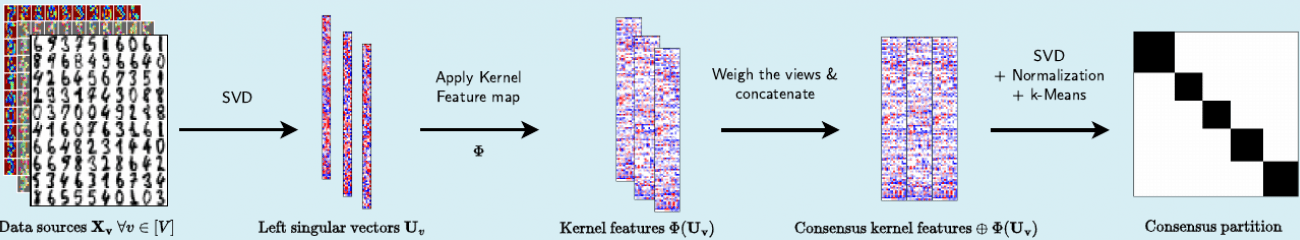
- Implicit consensus clustering. R. Boutalbi, L. Labiod, M. Nadif, Data Min Knowl Disc 35, 2313–2340 (2021)
- Regularized Bi-Directional Co-Clustering, S. Affeldt, L. Labiod, M. Nadif, Briefings in Bioinformatics, 22(2), 2021.
- Unsupervised and self-supervised deep learning approaches for biomedical text mining, briefing in Bioinformatics, M. Nadif, F. Role, 2021.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attack Mitigation in Internet of Medical Things, O. Salem, K. Alsubhi, A. Shaafi, M. Gheryani, A. Mehaoua, R. Boutaba, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 38(3), 2022
- Markov Models for Anomaly Detection in Wireless Body Area Networks for Secure Health Monitoring, O. Salem, K. Alsubhi, A. Mehaoua, R. Boutaba, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 39(2), 2021
Projects
- Project ANR GePhEx (S. Affeld, 2019) : Learning causal effects between phenome and exposome from large amounts of heterogeneous data in human complex diseases.
- Project ANSES MOLDASTH (R. Nadif, 2021) Moulds in dwellings, inflammation, immune response, and ASTHma endotypes in the CONSTANCES cohort.
- Project Emergence Idex Spectrans (M. Nadif, 2021). Specialised corpora and neural translation.
- Project CDC Informatique. (M. Nadif) Detecting anomalies and reversals in finance.
-
Project THALES (M. Nadif, 2019) Hybridization of AI algorithms with business knowledge for rail transportation.
-
Project SOPRA-STERIA and AIRBUS-APSYS. Security of Industrial Internet of Things based on Blockchain.
-
Project ORANGE LABS. Real-time Network Service Detection, Classification and Analysis from encrypted real-time traffic communications